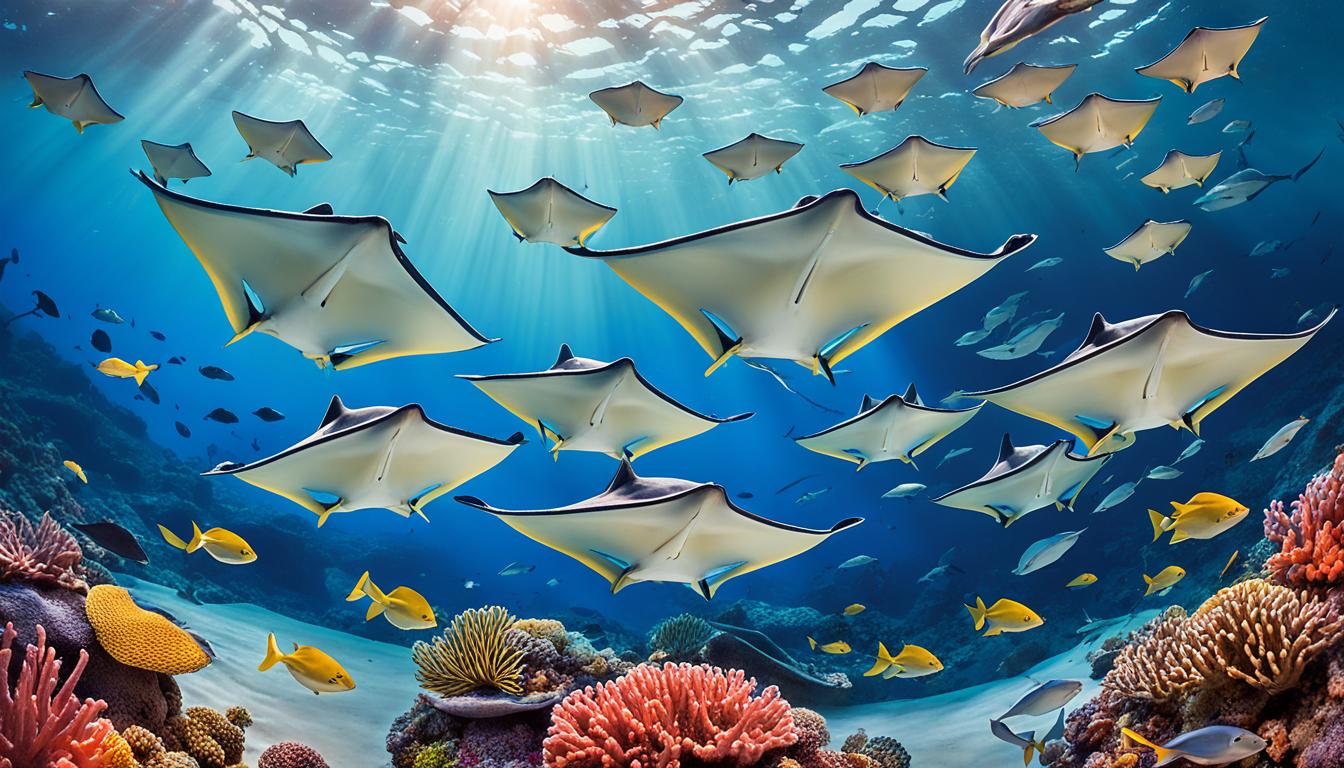
Have you ever wondered what stingrays eat? Well, get ready to uncover the secrets of these intriguing creatures’ diet. From their natural prey to their unexpected culinary choices, stingrays have a diverse range of food preferences that will leave you amazed.
Stingrays are fascinating underwater creatures that can be found in oceans and seas around the world. They have a unique mouth structure that allows them to consume a variety of prey, making them skilled hunters in their underwater habitats.
So, what exactly do stingrays eat? Let’s dive into the world of these majestic creatures and discover the truth.
In the following sections, we will explore the natural diet of stingrays, the surprising vegetarian species among them, their opportunistic feeding habits, their scavenging abilities, and how human interaction can impact their feeding patterns. So, stay tuned to learn more about these captivating creatures and their eating habits!
Stingrays’ Natural Diet
Stingrays have a diverse and natural diet that consists mainly of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. They are known to feed on benthic invertebrates, such as shrimp, crabs, and clams, which they can easily catch using their specialized mouth structure.
Stingrays are highly adapted to their feeding habits, allowing them to efficiently capture their prey. Their flat bodies and long, whip-like tails help them navigate through the water, while their mouths are specifically designed to crush and consume their preferred food sources.
These graceful creatures are expert hunters, using their excellent senses, including electroreception, to locate their prey buried in the sand or hiding in the nearby water column. Once the stingray detects an unsuspecting target, it swiftly closes in for the kill.
Furthermore, stingrays possess unique dental adaptations that further aid in their feeding. Their teeth are specially designed to crush the hard shells of crustaceans and mollusks, ensuring no part of their meal goes to waste.
Stingrays’ natural diet consists of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Their specialized mouth structure allows them to capture and consume benthic invertebrates such as shrimp, crabs, and clams.
By relying on their natural diet, stingrays ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients to thrive in their marine environments. The consumption of small fish provides them with a good source of protein, while crustaceans and mollusks offer essential minerals and vitamins. This balanced diet supports their growth, reproduction, and overall wellbeing.
To visualize the diversity of the stingray’s natural diet, take a look at the following table:
| Food Source | Examples |
|---|---|
| Small Fish | Sardines, Anchovies |
| Crustaceans | Shrimp, Crabs |
| Mollusks | Clams, Mussels |
| Other Benthic Invertebrates | Worms, Squid |
Stingrays’ natural diet is not only essential for their survival but also contributes to the balance and health of their ecosystems. As apex predators, they play a vital role in controlling populations of smaller fish and invertebrates, ensuring the overall stability and biodiversity of their underwater habitats.
Key Takeaways:
- Stingrays’ natural diet primarily consists of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks.
- Their specialized mouth structure enables them to capture and consume benthic invertebrates.
- Stingrays’ dental adaptations allow them to crush the hard shells of their prey.
- Their diet provides essential nutrients for their growth, reproduction, and overall wellbeing.
- By consuming a variety of prey, stingrays contribute to the balance and health of their ecosystems.
Unexpected Vegetarian Stingrays
Stingrays are typically known for their carnivorous feeding habits, but did you know that there are some surprising exceptions to this rule? Yes, that’s right! Some stingray species have adopted a vegetarian lifestyle, feeding on sea grasses and algae to meet their dietary needs.
This unique adaptation sets them apart from other members of the ray family, showcasing the incredible diversity and flexibility of these mesmerizing creatures. Let’s take a closer look at these extraordinary vegetarian stingrays and their fascinating dietary preferences.

Vegetarian Stingrays: A Nutritional Surprise
The discovery of vegetarian stingrays was a surprising revelation for researchers who had long believed that these animals were exclusively carnivorous. These select species have evolved to obtain their essential nutrients from plant sources, primarily sea grasses and algae.
“The existence of vegetarian stingrays sheds light on the remarkable adaptability and resourcefulness of these aquatic creatures.” – Dr. Jane Wilson, Marine Biologist
Benefits of a Vegetarian Diet
By consuming sea grasses and algae, vegetarian stingrays are able to access a rich source of essential nutrients, including carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This diet provides them with the energy they need to thrive in their marine habitats, all while maintaining a unique ecological niche.
The Ecology of Vegetarian Stingrays
Vegetarian stingrays play a significant role in the marine ecosystem by serving as herbivores. Their feeding behavior contributes to the maintenance and propagation of sea grass beds, which are crucial habitats for numerous marine species.
Additionally, their diet helps control the growth of sea grasses, preventing overgrowth and maintaining a balanced ecosystem. Vegetarian stingrays play an important part in preserving the delicate equilibrium of marine environments.
Other Diet Considerations
While vegetarian stingrays primarily rely on sea grasses and algae for sustenance, it’s important to note that this diet may vary depending on environmental conditions, availability of food sources, and individual preferences. Some vegetarian stingrays may supplement their diet with small invertebrates or other plant matter, showcasing their adaptability.
The Wonders of Stingray Diversity
The existence of vegetarian stingrays is a testament to the vast diversity of marine life and the incredible range of adaptations that occur within individual species. It serves as a reminder that there is always more to discover and learn about the fascinating world beneath the waves.
| Vegetarian Stingray Species | Natural Diet |
|---|---|
| 1. Potamotrygon orbignyi | Sea grasses, algae |
| 2. Taeniura meyeni | Sea grasses, algae, small invertebrates |
| 3. Neotrygon indica | Sea grasses, algae, plant matter |
Opportunistic Feeders
Stingrays are fascinating creatures known for their opportunistic feeding habits. As opportunistic feeders, they have the ability to take advantage of various food sources they come across. This adaptability allows them to survive and thrive in diverse marine environments.
Stingrays are skilled hunters, always on the lookout for prey. They have a specialized mouth structure that enables them to catch and consume a wide range of small marine organisms. Some of the preferred prey of stingrays include:
- Small fish
- Squid
- Octopus
These opportunistic feeders are not picky eaters. They will go after any small prey they can catch, using their excellent senses and stealth to their advantage.
Observing stingrays in action is a mesmerizing experience. Their fluid movements and lightning-fast strikes showcase their hunting prowess. Whether stalking a school of fish or ambushing their prey from beneath the sand, stingrays are highly efficient and successful hunters.
In their quest for food, stingrays also play an important role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. By preying on smaller organisms, they help control their population and prevent potential ecological imbalances.
Stingrays’ opportunistic feeding habits demonstrate their adaptability and resourcefulness. Their ability to take advantage of various food sources ensures their survival in an ever-changing marine environment.
Stay tuned for the next section, where we will explore the scavenging behavior of stingrays and how it contributes to their unique feeding habits.
Bottom-Dwelling Scavengers
When it comes to finding food, some stingrays have mastered the art of scavenging along the seabed. These remarkable creatures use their specialized mouths to dig into the sand or mud, relentlessly searching for buried prey. With their acute sense of smell and expertly designed bodies, stingrays are equipped to be efficient scavengers.
Scavenging behavior is crucial for the survival of certain stingray species in their marine habitats. By exploring the depths of the ocean floor, they are able to uncover hidden treasures — worms, mollusks, crustaceans, and other invertebrates that make up their diet. Their exceptional ability to locate and extract these buried organisms ensures their continued existence.
Stingray Scavenging Technique
Stingrays utilize a combination of sensory and physical adaptations to excel at scavenging. They possess barbels, which are slender sensory organs that protrude from their mouths. These barbels help stingrays detect chemical cues from potential prey buried beneath the sand or mud.
The process of scavenging involves sweeping their flattened bodies along the ocean floor, stirring up sediment to reveal potential sources of food. With their mouths positioned ventrally, stingrays employ a sucking motion to draw in prey hidden beneath the surface. They have developed a powerful crushing mechanism in their jaws that allows them to crush the shells of crustaceans and mollusks.
This scavenging behavior not only sustains stingrays but also contributes to the ecological balance of their marine ecosystems. They help maintain a clean seabed by consuming carrion and scavenging the remains of other creatures, preventing the buildup of organic matter.

Stingray Scavenging Adaptations
Stingrays have evolved specific adaptations that enable them to thrive as bottom-dwelling scavengers. Here are some notable adaptations:
- Flat body shape: Stingrays’ flattened bodies allow them to effortlessly glide across the ocean floor, maximizing their surface area in contact with the substrate.
- Ventral mouth position: Their mouths located on the undersides of their bodies facilitate efficient feeding while remaining close to the seafloor.
- Edged teeth: These teeth are well-suited for crushing the hard shells of their scavenged prey.
- Barbels: The barbels, equipped with numerous taste buds, help stingrays sense and locate hidden food sources.
Through their scavenging abilities, stingrays not only survive but also play a vital role in maintaining the health of their underwater habitats. By understanding and appreciating these fascinating creatures, we can better protect their environment and ensure their continued existence.
| Stingray Scavenging Adaptations | Description |
|---|---|
| Flat body shape | Enables easy maneuverability along the seabed. |
| Ventral mouth position | Facilitates efficient feeding while remaining close to the seafloor. |
| Edged teeth | Perfectly suited for crushing the hard shells of scavenged prey. |
| Barbels | Equipped with taste buds, helping stingrays sense and locate buried food sources. |
Human Interaction and Feeding Habits
Stingrays’ feeding habits can sometimes bring them into contact with humans. In certain tourist destinations, people may feed stingrays to attract them. While it may seem harmless, this behavior can disrupt their natural feeding patterns and cause dependency on human handouts.
Feeding stingrays may provide an exciting opportunity for human interaction, allowing people to get up close and personal with these magnificent creatures. However, it is important to consider the potential consequences of this interaction on the stingrays themselves.
Stingrays have developed unique feeding habits that are finely tuned to their natural marine environments. They have specific hunting techniques and prey preferences that ensure their survival and maintain the balance of the ecosystem they inhabit.
When humans interfere with the feeding habits of stingrays by providing them with food, it can lead to a disruption in their natural behavior. Dependence on human handouts can make the stingrays reliant on these unnatural food sources, potentially affecting their overall health and well-being.
Furthermore, the act of feeding stingrays can alter their natural feeding patterns and hierarchy. It may result in competition among the stingrays, as they fight for the artificially provided food. This can lead to aggression, injuries, and even the exclusion of some individuals from accessing food.
Additionally, when stingrays are fed by humans, it can result in an increase in their population in certain areas. This can lead to environmental imbalances, as the ecosystem may not be able to support the larger number of stingrays due to the artificial abundance of food.
It is crucial to remember that although human interaction with stingrays can be fascinating and provide memorable experiences, our actions should prioritize the well-being and preservation of these magnificent creatures. Instead of feeding them, we can contribute to their conservation by supporting initiatives that focus on habitat protection, research, and education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stingrays have a diverse diet that includes small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, sea grasses, and algae. They are opportunistic feeders and skilled hunters, able to adapt to various food sources. Stingrays use their specialized mouth structures to catch benthic invertebrates such as shrimp, crabs, and clams.
Although some stingray species have a unique vegetarian diet, feeding on sea grasses and algae, the majority of stingrays are carnivorous and rely on hunting for survival. Their scavenging behavior along the seabed allows them to dig into the sand or mud, searching for buried prey like worms and other invertebrates.
While it may be tempting to interact with stingrays by offering them food, it is crucial to respect their natural feeding habits. Unnecessary human interaction and feeding can disrupt their dietary needs and lead to dependency on handouts. To preserve the delicate balance of their marine environments, it is important to appreciate and observe stingrays’ feeding habits from a distance.